Flash Flood Watch
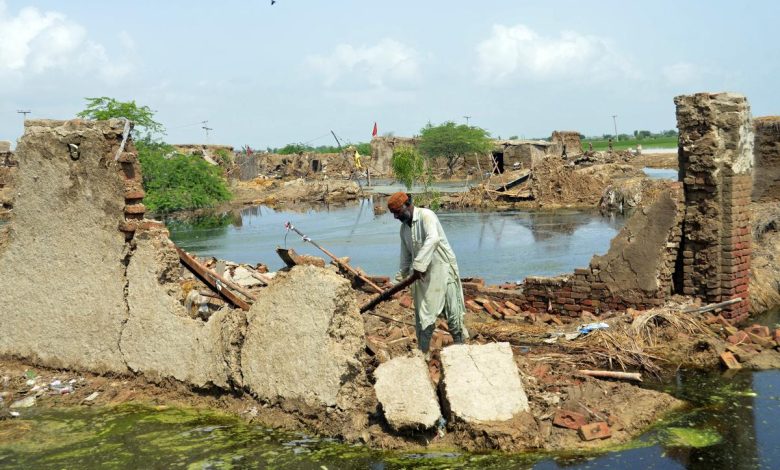

Flash flooding is the rapid flooding of low lying areas. It can be washes or rivers, lakes or dry lakes. This can happen due to heavy rain or storms, meltwater from snow or ice flowing over snowfields or ice sheets, or severe thunderstorms. Flash floods could also occur following the collapse or damage to a natural -ice dam or debris dam . Flash floods can occur after the collapse of a natural a href=”https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ice_jam” title=”Ice jam”>ice or a human structure such as a man-made a href=”https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Johnstown_Flood” title=”Johnstown Flood”>Johnstown Flood/a> in 1889. Flash floods can also cause large amounts of sediment to be deposited on floodplains. This can lead to the destruction of vegetation not adapted for flood conditions.
Causes
Flash flooding of a road in Northern Mexico after a thunderstorm lasting about 3-5 hours. These flash floods usually occur in areas that have received rain but can be seen downstream from the source. Flash floods are also common in areas close to volcanoes. These flash floods occur when icebergs melt under intense heat. Flash floods have been known to occur in the highest mountain ranges in the United States. Flash flooding can also result from heavy rains caused by hurricanes or tropical storms. A large amount of water can be released from dams that fail and damage everything around it.
Hazards
A flash flooding can cause a large flood to inundate a small ditch, flood barns, and tear out newly installed drain pipes. Flash floods are often underestimated by many people. Flash floods are characterized by their quick nature and rapid-moving waters. The vehicle is not designed to protect against the flood, but it can make people feel more confident and less likely that they will be swept away by the flash flooding. Flash floods can cause more than half the deaths of people who cross them. Arid areas are less likely to experience storms, but they can bring large amounts of water within a short time. A second problem is that storms in dry regions are often very rare, but they can produce a lot of water quickly. Sometimes desert roads cross creek beds and dry rivers in certain areas. The driver may not realize that desert roads cross dry creek beds and rivers. The flood sweeps through canyon, making it difficult for hikers to get out of the way and avoid the flood. One example: A cloudburst on 14 September 2015 in southern Utah resulted 20 flash flood deaths. Seven of those fatalities were at Zion National Park where hikers became trapped in a slot canyon by floodwaters.
Flash flood impacts
Flash floods can have severe consequences for both the built environment as well as the natural environment. The devastating effects of flash flooding can have a wide range of impacts, including damage to buildings and infrastructure as well as on vegetation, livestock and lives. It is particularly difficult to determine the effects in urban areas. Researchers have used datasets, such as the Severe Hailstorms Analysis and Verification Exercise (SHAVE), and the U.S. National Weather Service storm Data datasets to compare the impact of flash flooding with the physical processes involved. This should improve the reliability of flash flooding impact forecasting models. Analyse of flash floods in America between 2006 and 2012 revealed that deaths and injuries are most common in rural areas.
fatalities and injuries
An Impact Severity Scale is proposed for 2020. This scale provides a consistent overview of flash flooding effects. It categorizes impact types and severity, maps their spatial extent and shows how they are distributed across the floodplain. The following categories are used to classify flood effects based on their severity: (i. Impacts on built environment; (ii. Impacts on man-made objects); (iii.) Impacts on the natural environment (including agriculture, vegetation, and pollution) and finally (iv.) Impacts on the human population (entrapments and injuries, fatalities). The scale was created to aid in prevention planning. It can be used to classify flood effects into four categories: (i) impacts on the built environment, (ii) impacts on man-made mobile objects, (iii) impacts on the natural environment, including vegetation, agriculture, and pollution, and (4v). Impacts on the human population (entrapments, injuries, fatalities).g